Content:
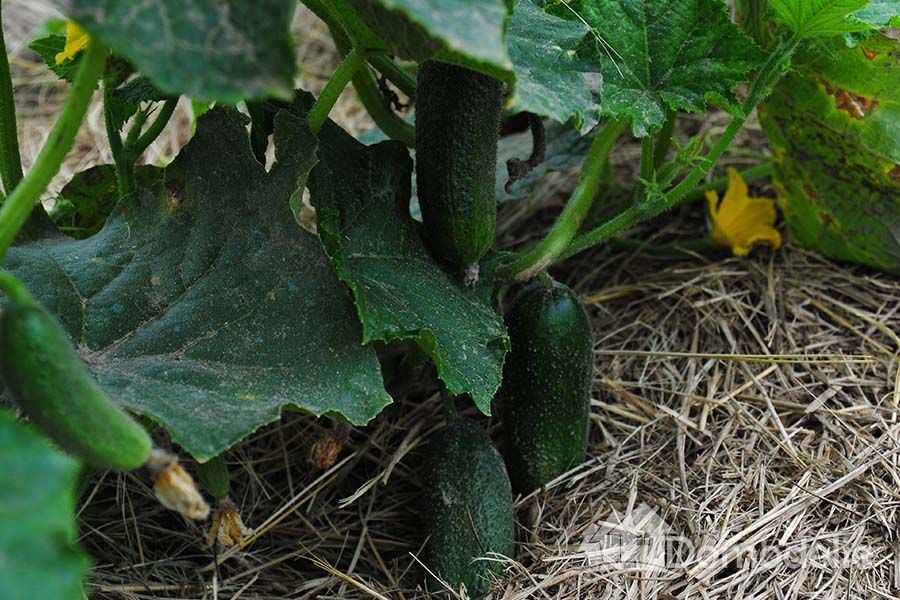
Growing cucumbers in a greenhouse has a number of advantages compared to growing cucumbers. The most significant advantage of greenhouse cucumbers is that already the first harvest can be obtained 35 days after planting, and then cucumbers can be harvested all year round. To achieve maximum success, it is necessary to have knowledge of the correct cultivation of cucumbers in a greenhouse:
- selection of equipment - comparison of a greenhouse and a greenhouse;
- selection of varieties of cucumbers for indoor cultivation;
- selection of soil and preparation for planting cucumber seedlings;
- seed preparation;
- growing seedlings and planting them in a greenhouse;
- agrotechnical features of growing greenhouse cucumbers;
- pest protection and disease prevention.
Preparing for growing cucumbers in a greenhouse
How to grow cucumbers in a greenhouse? The preparatory work for starting the cultivation of cucumbers in the greenhouse can be broken down into steps or steps that must be taken to effectively cultivate cucumbers with a bountiful harvest all year round.
The first stage is the choice of equipment. Which is better: a greenhouse or a greenhouse, what are their differences? It should be noted here that cucumbers can be grown year-round in the Central, South and Volga regions, as well as under unfavorable climatic conditions using greenhouse buildings.
There are two types of buildings designed to increase yields and extend the cultivation period:
- A greenhouse is a simpler building, small in size, 1-1.5 m in height, receiving heating from the sun and due to the heat of decomposition of humus and manure. There are no doors in the greenhouse, access to the crops being grown, as a rule, is simply folding the film from the top or side. Growing cucumbers in a greenhouse is a great option because the greenhouse method of cultivation is most often used when planting seedlings before transplanting into the ground, so that it gains strength, or for germinating seeds. In the greenhouse, the air heats up quickly and creates a beneficial effect on the young growth of plants.
- A greenhouse is a frame structure with soil protection with heat-preserving characteristics. The recommended height of the greenhouse for growing cucumbers is 2.5 m. There is no limit in the height of the greenhouse, the purpose of use is taken into account here. So, for summer cottages for the purpose of growing cucumbers for home use, a rather small greenhouse is enough, and in business, a higher greenhouse is needed for sales, in which agricultural machinery can be freely located.
There are three types of greenhouse cover:
- Polycarbonate is lightweight, durable, retains heat well in early spring, but not enough in winter. In greenhouses with such a coating, in winter it is necessary to install additional heating equipment, such as wood, gas or electric.
- Glass is a heavy coating, so a metal frame is required. Glass covered greenhouses can be used all year round.
- The film is the lightest material, the frame for it can be either wood or wire. Greenhouses with this cover are mainly used in summer cottages for seasonal cultivation and early harvest.
So, taking into account the requirements for obtaining a crop (for business or home use) and climatic conditions, it is necessary to choose equipment where cucumbers will grow.
The second stage is choosing a variety of cucumbers.In indoor conditions, self-pollinated cucumbers and hybrids (parthenocarpic) are suitable for growing. Varietal cucumber can be planted from year to year by harvesting the seeds yourself. Hybrids are seedless species or containing empty seeds without an embryo. The hybrids are marked F1 when purchased. The main advantages of hybrids are:
- high acclimatization;
- high resistance to pests and diseases;
- faster ripening times;
- the yield is 30-40% higher;
- transportability.
Popular varieties of cucumbers for the greenhouse
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Varietal cucumbers | |
| Pace | 1) sweet early maturing; 2) with bundle ovaries; 3) dense, crunchy without bitterness; 4) average weight - 80 g; 5) universal use. |
| Courage | 1) Dutch, introduced in 1980; 2) harvest from a bush - 25 kg; 3) universal use. |
| Sigurd | 1) strong root system; 2) dark green, densely lumpy; 3) average length up to 13 cm; 4) when planting seedlings, the distance between the bushes should be at least 1.5 m. |
| Serpentine | 1) short lashes with small fruits up to 8 cm; 2) fruiting after 36 days; 3) many ovaries (6-8) on the knot; 4) can be used for preservation. |
| Valaam | 1) super-early - ripens in 35 days; 2) cold-resistant; 3) large lumpy with black spines; 4) does not taste bitter. |
| Hybrids | |
| Courage F1 | 1) fruiting - after 45 days; 2) dark green with light stripes; 3) planting seedlings with a density of 3 bushes per 1 m²; 4) yield from 1 m² - 7-8 kg; 5) universal use. |
| Benefit F1 | 1) fruiting - after 50 days; 2) cucumber length up to 13 cm; 3) dark green with small frequent tubercles; 4) sweet, strong, without bitterness; 5) good for salting. |
| Alekseich F1 | 1) early maturing - after 37 days; 2) bundle ovaries; 3) green medium tuberous; 4) average length - up to 8 cm; 5) yield - 12-15 kg / m²; 6) universal use. |
| Emelya F1 | 1) early maturity - after 40 days; 2) bundle ovaries; 3) the growth of the lashes is not limited; 4) bright green, large tuberous with white thorns; 5) planting seedlings with a density of 3-4 bushes per 1m²; 6) fresh application and conservation. |
| Dynamite F1 | 1) early maturing - after 40 days; 2) tuberous with white spines; 3) average length - 12-15 cm; 4) weight up to 120 g; 5) harvesting - 7 kg / m²; 6) universal use. |
The third stage is preparing the soil for the greenhouse. Cucumbers are very fond of loose and fertile soil that retains moisture, which is very important for cucumbers who like to "drink". The best soil composition for a greenhouse is:
- sod land - 3 parts;
- humus or matured compost - 2 parts;
- sand - 1 part.
Before sowing cucumbers and / or planting seedlings, add 1 liter of vermiculite to 10 kg of prepared soil to enhance looseness, ash - 1 glass, superphosphate - 2 tbsp.
The fourth stage is the preparation of seeds for sowing when choosing this method of planting cucumbers or growing seedlings.
Disadvantages of seed planting of cucumbers in a greenhouse:
- longer vegetative period;
- less yield due to longer growing season;
- 30% of seeds may not sprout;
- a high risk of freezing plantings when frost returns;
- requires more care - constant ventilation, shelter of seedlings, control of soil and air temperatures.
To reduce the risks when planting with seeds, you must:
- use a greenhouse with a polycarbonate cover, as it heats up faster and retains heat well;
- use additional heating in the greenhouse (except for the sun);
- choose early varieties of cucumbers to shorten the growing season;
- sow 2 seeds into the hole - remove the weaker sprout in the future.
Agronomists give the following recommendations for planting cucumbers by seeds:
- before sowing, the temperature should be at least 12-13 ° C even at night, and after the appearance of the first leaves - at least 15 ° C around the clock. At a lower temperature, the seeds will die;
- in the middle lane, sowing with seeds should be carried out from April 20 to May 10;
- do not allow planting density - this will reduce yield;
- the beds should be 30 cm high - planted in two rows with an interval of 50 cm, the distance between the beds should be at least 90 cm;
- lay the seed flat to a depth of 2 cm in a well spilled with water, then sprinkle the hole with earth to the level of the bed;
- cover the beds with cut plastic bottles and remove every day for airing;
- conduct constant monitoring of the temperature regime of soil and air.
In the future, the plantings are looked after in the same way as when planting seedlings.
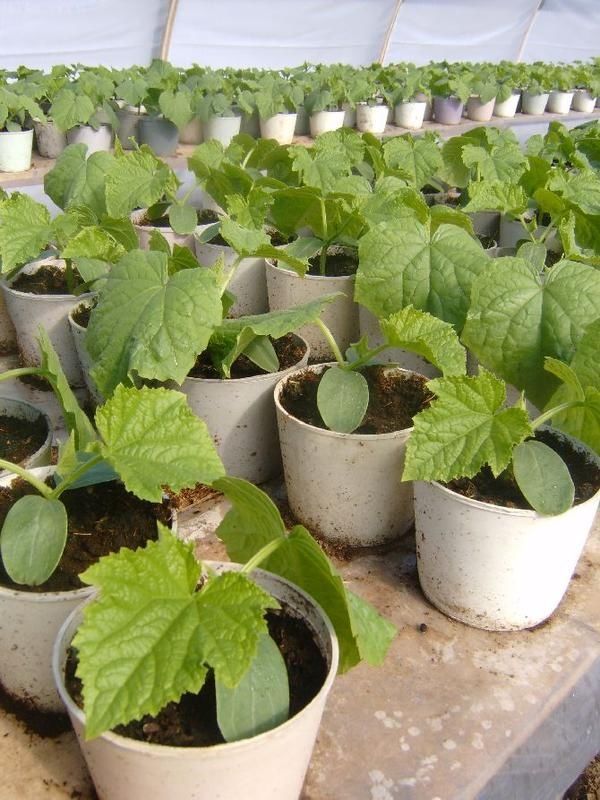
Growing seedlings. For sowing, take separate cups for the correct formation of the root system. The seeds must be germinated before planting in the hole, which in turn must be spilled with a weak solution of potassium permanganate. Sprinkle the seed with a two-centimeter layer of earth.
Cover the cups with polyethylene for 2-4 days until sprouts appear.
The fifth stage is planting seedlings. Plant the seedlings in the greenhouse when the soil temperature reaches + 15 ° С. Seedling planting rules:
- make a depression in the hole with fertilizer for the size of the cucumber rhizome;
- deepen the seedlings to the first leaf;
- observe the distance between the seedlings - at least 50 cm, and depending on the variety, it can reach 1.5 m;
- compact the soil around the seedlings.
To speed up the production of the first ovaries, special care is required for young cucumber shoots in the greenhouse.
Necessary conditions for the cultivation of cucumbers
| Condition | Recommendations |
|---|---|
| Watering and moisture | 1) cucumbers love moisture very much. Water regularly and often, watch out for the leaves - the first sign of a lack of moisture is wilting. 2) Drip irrigation is recommended, as it provides stable air humidity in the greenhouse. 3) water consumption - 20 liters per day per 1 m². in case of ovary formation, increase the consumption to 30 liters per day. 3) the water should be settled, not cold. |
| Top dressing | 1) when growing seedlings, use only ash. 2) before planting seedlings in the greenhouse, fertilize it with a complex mineral fertilizer to build up green mass. 3) after planting in the greenhouse, do not "feed" for 10 days to allow the seedlings to take root in a new place. 4) then feed with solutions of mullein, chicken droppings and ash. 5) apply potash fertilizers during the flowering period. |
| Temperature | 1) in the greenhouse, the temperature must be maintained at + 17 ° C. 2) during disembarkation of seedlings - + 25 ° С. 3) when the temperature rises above 30 degrees, ventilation and spraying of bushes with cucumbers is necessary. |
| Airing | until the seedlings get stronger, it is better to refuse airing, since young bushes are afraid of drafts. |
| Light mode | 1) light affects productivity - cucumbers need 12 hours of daylight during the intensive growing season. 2) if there is a lack of light, artificial lighting should be provided, this is especially important during the fruiting period. |
Methods for growing cucumbers in a greenhouse
To obtain a high yield, additional care for cucumbers in the greenhouse is necessary:
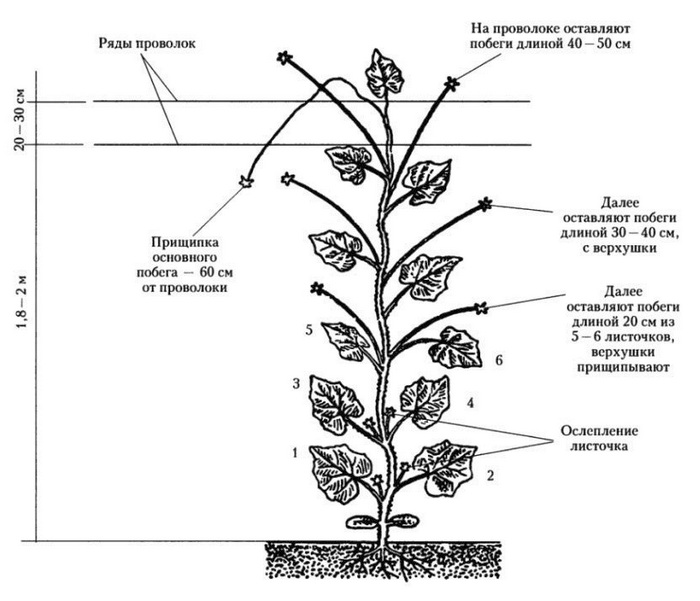
- Formation and pinching (docking) of the lashes is done as follows: at the first 45 cm - completely blind the shoots, that is, leave only the stem and lateral shoots; the next 45 cm - pinching over the first leaf; then for the next 45 cm - above the second, above the third, and so on leaves.
- Grasshopping - remove stepchildren at the beginning of the growth of the bush at a distance of ½ m above the soil level, higher it is dangerous to do this, since ovaries are formed on the side lashes. After this work, the cucumbers receive more strength for further growth. Recommendations: bend the leaf and carefully remove the shoot with a knife.
- Tying is carried out for the availability of lighting, airing the lashes, so that there is no weaving between the bushes and to simplify the care of plants.
A rope or twine is taken, one end of which is attached to the ceiling of the greenhouse, and the other is attached between the lower leaves. As the bush grows, the whip is wrapped clockwise. When tying up, a trellis net is often used - this is a plastic cloth with cells. Cucumbers with antennae independently catch on the cells and direct growth upward.
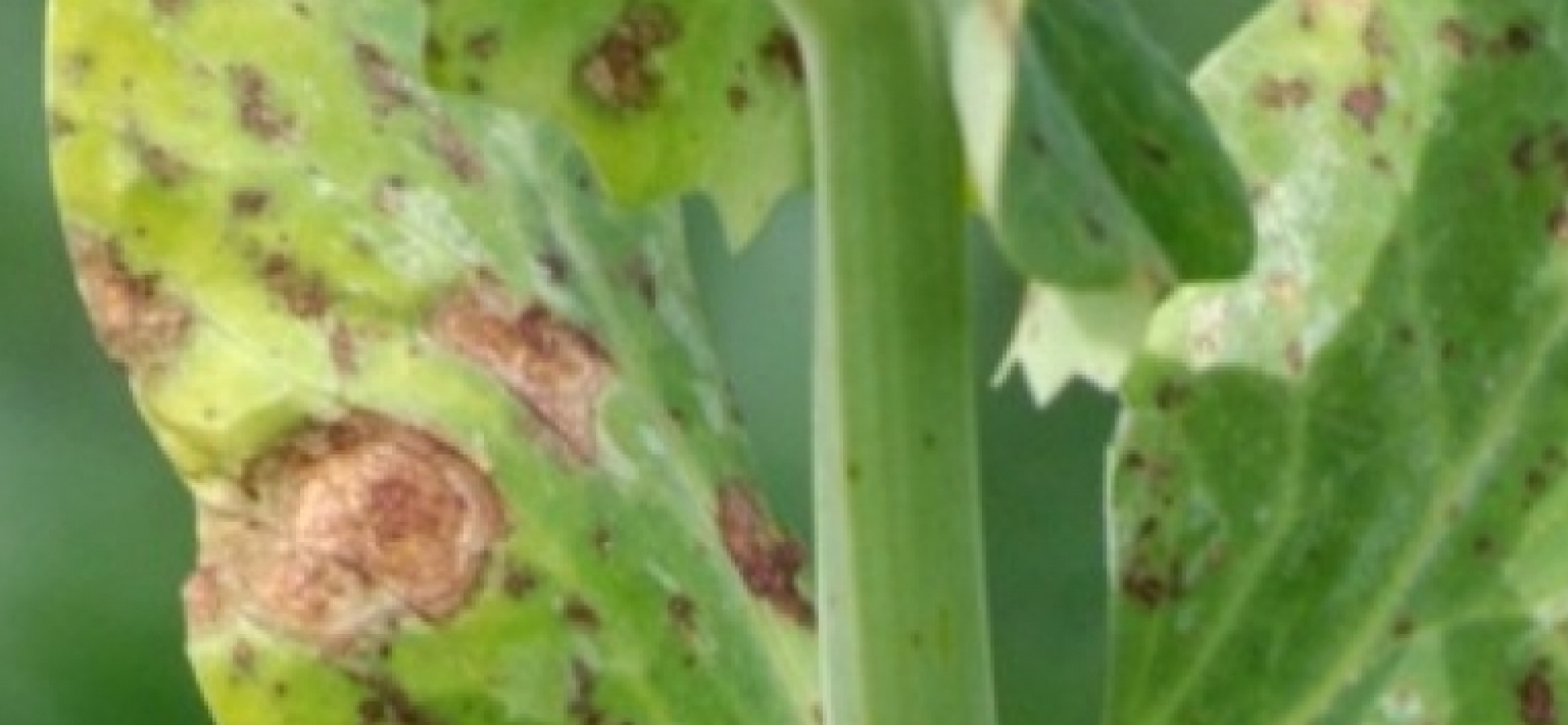
- Disease and pest control. Cucumbers grow in moisture, and this is a seedling environment for pathogenic fungi, viruses, bacteria that can cause serious diseases, such as:
- Ascochitis - occurs most often during fruiting. The leaf at the edges is covered with gray light spots with the further appearance of black dots, small brown spots are observed on the stem and shoots. The fruits turn black. Ways of struggle: spray with a solution of copper sulfate - 5 g per 10 l of water + urea solution - 10 g per 10 l of water.
- Cladosporium or olive spot on young cucumbers. They become bent and covered with dark brown spots. Treat the bushes with a 0.3% solution of copper oxychloride every 10 days 3 times.
- Root rot is formed with excessive moisture, the root system becomes weak, the stem becomes thin, followed by drying out. Control: Pollination of the lower part of the stem with sawdust, sand, peat or chalk. Reduce watering. It is better to remove the diseased plant from the garden, so as not to infect healthy cucumbers, pour bleach on this place at the rate of 120 g per 1m² and loosen the soil.
Cucumbers are not a very demanding crop. They grow well indoors, subject to the rules of planting, watering, feeding and providing protection from pests and diseases.
Proper cultivation of cucumbers in a greenhouse will ensure a high yield.