Content:
Anyone who breeds rabbits knows how troublesome it is to give birth and raise babies. Despite the fertility of animals, part of the offspring dies at an early stage: some freeze, others do not have enough nutrition.
Bunnies are often to blame. One female does not have milk, another mother may simply refuse to feed the babies. There are also females who, not having time to give birth, die. To preserve the brood, you need to know how to feed rabbits without a rabbit.
Is it possible to do without a rabbit
Newborn rabbits are still nude and for the first days are under the mother's cover, continuously sucking on the breast. A two-week-old rabbit is already covered with a tender short fluff and begins to crawl out of the nest.
The farmer does not even have a question of how to feed rabbits without a rabbit at 14 days of age. Babies are already partially switching to food intended for the mother. But how to feed a very small sucker if mom is not around?
How to plant in someone else's nest
If there is more than one rabbit on the farm, and lambing occurred almost at the same time, you can save the babies who had to be left without a mother by placing them in another nest. In order for the nurse to accept other people's children, they are first rubbed with the fluff of the named mother (you can take it in the nest itself) - this will help to interrupt the unfamiliar smell.
The lining of the babies should be done in the very center of the nest so that the planted baby mixes with the native rabbits. This will help trick the rabbit. But the number of other people's babies should be limited, otherwise the mother will not have enough milk for all the babies, and she may quit feeding them. Then you will have to solve the problem of how to feed other newborn rabbits.
How to replace rabbit milk
When the rabbit has poor lactation, or the mother completely refused to feed the babies (or died), the breeder raises the question of artificial nutrition. Novice farmers ask how to feed the rabbits with cow's milk? Although it would be more correct to ask what is better to replace the breast diet.
Rabbit milk substitutes
| What to replace | Features: |
| Goat milk | Fresh goat product is similar in composition to rabbit. Unless they differ slightly in fat content. Therefore, you will not have to mix milk with anything during feeding. |
| Milk substitutes for animals | You can find milk formula for small animals in veterinary pharmacies. If it is not possible to buy a replacement for rabbit milk, then you can choose complementary foods for dogs or cats. These nutritional mixtures are almost the same in composition and are well absorbed by rabbits. |
| Food fusion for kids | As an option - dry mixes for small children. But you should choose the products that contain the least amount of additives and sugar (for example, "Baby", "Baby", "Nutrilon") |
As for cow's milk, this is the most extreme case.As a cow and a rabbit differ in biological characteristics, so does their lactose differ in composition. In order for little rabbits to be able to digest cow's milk, it is recommended to dilute it with sugar-free condensed milk in a 4: 1 ratio.
Feeding rules
Sometimes breeders have to take charge of the feeding of the rabbits. The first week is the most difficult for babies. Usually the rabbit covers the newborns with her hair. Left alone, naked rabbits begin to freeze and may die.
Another difficulty in nursing cubs is that the two-week-old rabbit is still blind, so it is completely unable to navigate in space. The owner himself must bring and pour food into him.
Having decided what to feed the newborn rabbits with, the farmer begins the duties of a nurse, following the following rules:
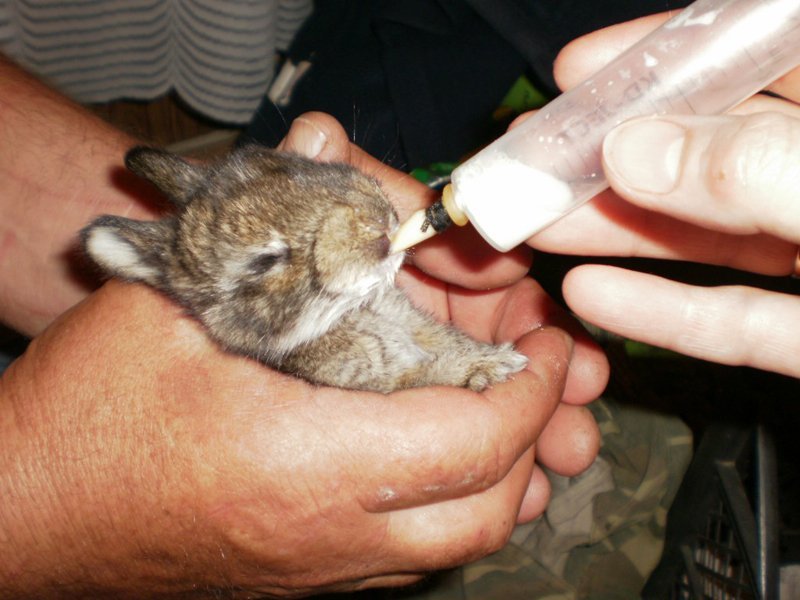
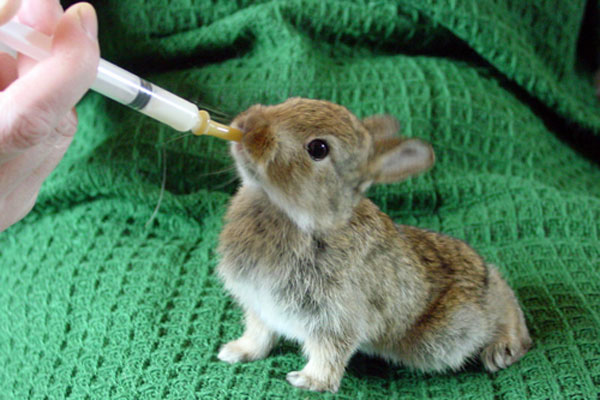
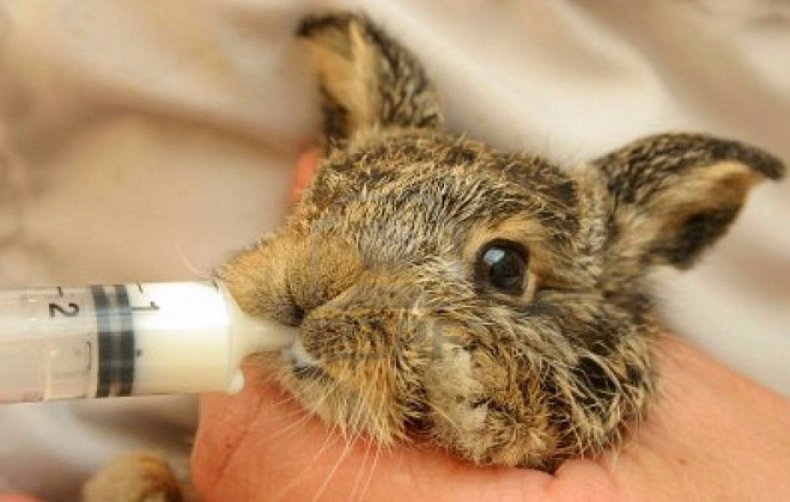
- To begin with, choose which tool is most suitable for feeding:
- small baby bottle;
- syringe (without needle) for 20 cubes;
- a bottle of eye drops or a large dropper.
- Artificial feeding should be as close as possible to the natural process; only then will the rabbits develop natural instincts;
- Blind newborns do not react well to a rubber nipple, so milk formulas have to be forced into their mouths;
- To prevent the baby from choking, the liquid is served in small portions;
- For 2-3 days, the rabbit is first lubricated with liquid around the mouth - he will already lick the milk himself;
- When the rabbit revives, feeling the taste of food, they begin to pour milk into the mouth drop by drop; a newborn baby can eat no more than a milligram for 1 meal;
- Do not overfeed the cubs - this leads to problems with the stomach and respiratory tract;
- During feeding, the rabbit is kept in an upright position, without crushing its body.
To understand whether the baby is full or not, they are watching him after feeding. If the rabbit is restless, trying to find its mother, and at the same time squeaks, you can feed it a little more. A well-fed cub will quickly calm down and fall asleep.
Artificial feeding by age
The body of rabbits develops every day, rebuilds, and the digestive system also changes. Despite the fact that a 15-day-old cub can already eat a little of adult food, it is better to avoid this when artificial feeding rabbits. For the first month, babies are recommended to give exclusively milk or formula.
Age-appropriate feeding
| Period after birth, days | Features: | Milk norms, per feeding / per day, g. |
| 1-5 | · In the 1st visit, the baby is given 1 drop of nutrient fluid. During the day, 6 runs are carried out, each time increasing the number of drops; · From the 2nd day they feed 5 times; · On the 3-5th day, the number of calls is equal to 4. At this stage, the baby has not yet developed a swallowing reflex, with proper feeding, the rabbit should by the end of the period gain weight equal to 2 birth weights (approximately 120-180 g) | 1/5-6 |
| 6-14 | The entire period is fed 3 times, gradually increasing the dose. By two weeks, the baby should weigh 200-260 g. | 5/20-25 |
| 15-30 | Rabbit cubs are transferred to two meals a day. But, if the baby does not eat enough for the first 2 days, then 1 more visit is allowed. The average weight by the end of the month should be about half a kilogram | 10-13 / 20-26 (15-20 days); 15-25 / 30-50 (21-30 days) |
Switching to solid food
To make the transition to a new food more organic, solid food is introduced into the diet in small portions from 21 days from the moment of birth. To begin with, they take clean hay and monitor the condition of the kids. In case of intestinal upset, the experiment is stopped, returning exclusively to the dairy diet.
If the hay did not cause diarrhea, you can gradually introduce fresh grass, then a little feed, then grated carrots. You should not rush to a variety of diet - everything should go smoothly.
When the babies reach one month of age, milk is completely removed from the diet, transferring the rabbits to adult food. But, if it was not possible to feed the baby normally, and he does not gain his weight, the mixture can be served for another couple of weeks.
At this stage, only hay and water remain the basis of nutrition. Vegetables (carrots, potatoes, turnips, broccoli, cabbage leaves) should be ½ of the volume of hay, dry food - a small part.
Useful feeding
Breast milk provides babies with all the elements they need for development. In this regard, artificial feeding of rabbits can be considered not entirely complete. Many mixtures include some of the important components, but it is recommended to add various dressings to the milk.
Healthy Supplements
| Name | Features: |
| Fish oil + vitamin D | Oil drops are added to milk on the 1st day of life, having coordinated the dose with the veterinarian |
| Oat sprouts and flour | They are a source of vitamins B, E, PP and dietary fiber. A small pinch of flour is introduced into the mixture from the 5th day of life. From a month they are replaced with seedlings (50 g per day) |
| Table salt | The daily norm is 0.5 g. From the 30th day, granules are dissolved in drinking water and moistened with solid food. |
| Chalk, bone meal | They begin to give from the 20th day in the form of powder or small stones, 1-2 g each. |
| Birch, coniferous branches | They strengthen teeth well and are a source of vitamin C. 2 small twigs are enough for one month old rabbit |
| Cecotrophs | This is a litter of adult rabbits, containing fiber, proteins, vitamins B and K. 2 peas are dissolved in milk and given once a day, starting from the 10th day. With early introduction of hay into the menu, it is recommended to mix it with dung peas so that the rabbits have normal stools. |
| Acidophilus | The supplement is saturated with live bacteria, which are necessary for the establishment of the digestive process. Sometimes they are replaced with ordinary yoghurts, but then you need to carefully monitor the stools of babies |
As good as supplements, formula and milk from other animals are, they cannot completely replace native lactose. Therefore, any artificial nutrition cannot be considered balanced.
Forced training in the swallowing reflex is considered a significant drawback. Therefore, its formation can slow down, and sometimes cause difficulties. With the wrong actions of the breadwinner, the baby can be physically harmed.
The breeder himself experiences inconvenience:
- in the desire to leave the babies left without a mother in the first weeks, you have to conduct round-the-clock control over the rabbits;
- it becomes necessary to rebuild the compartment with babies in such a way that daylight does not interfere with them (under normal conditions they hide in the shadow of their mother);
- you need a special heating, allowing you to improvise the warmth of your own nest;
- sometimes problems arise with the selection of a rabbit milk substitute; it is important to have a trusted supplier;
- observance of maximum hygiene is required when communicating with the breeder with the cubs - all feeding equipment must be sterile, this will help to avoid intestinal infections;
- little rabbits do not know how to empty themselves, mothers usually help them in this, licking their tummies with their tongue; the breadwinner will have to massage the baby after each session;
- after the rabbit has eaten, it must be washed - milk must not be allowed to dry on its face.
But there is also merit in artificial feeding. After feeding, the animals are not so demanding on food, they quickly get used to the new diet, do not ignore feeding. As a rule, they always have a good appetite and quickly learn the feeding schedule.